Hemorrhagic Gastroenteritis in Dogs
HGE

SUMMARY OF CONTENT
SEVERITY:
-
 Can resolve with prompt and sufficient medical treatment
Can resolve with prompt and sufficient medical treatment -
 Treatable by a veterinarian, often requires hospitalization
Treatable by a veterinarian, often requires hospitalization -
 Daily probiotics, a high-quality diet and avoiding situations that may be stressful may help prevent HGE, however, the cause is not completely known.
Daily probiotics, a high-quality diet and avoiding situations that may be stressful may help prevent HGE, however, the cause is not completely known. -
 Transmission is not possible between animals and not possible between animals and humans
Transmission is not possible between animals and not possible between animals and humans -
 Diagnosis requires physical exam, blood testing
Diagnosis requires physical exam, blood testing
VERY COMMON IN
Symptoms & Signs
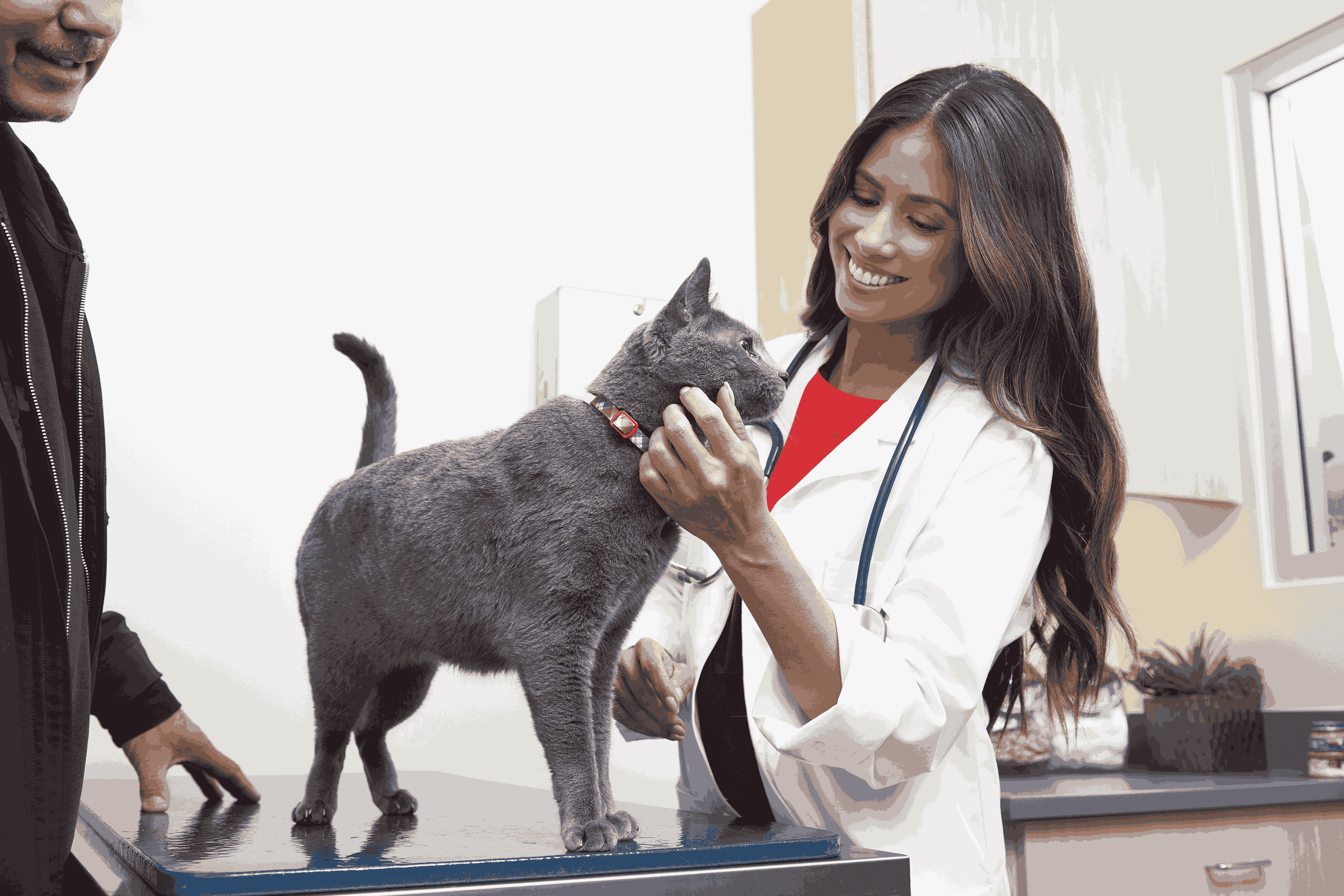
Dogs affected with HGE will often have a sudden onset of profuse, bloody diarrhea with a foul odor. Pet parents may also notice vomiting, decreased appetite, lethargy and abdominal pain. HGE in dogs often occurs very rapidly and can occur without a change in the dog's diet, environment, or routine. A fever with HGE is uncommon. HGE can affect dogs of any breed, gender or age although younger (2-4 year old) toy and miniature breeds appear to be predisposed; stress and hyperactivity in these breeds may play a role in this syndrome.
Diagnosis
Your veterinarian will begin with a physical examination of your pet. If HGE is suspected after the physical examination and history, your veterinarian will draw blood and perform a complete blood count (CBC) and often a chemistry panel to check organ function. If your dog’s CBC shows a total red blood cell level (PCV) of 60% or greater, and has all the clinical signs of HGE, a tentative diagnosis of HGE can be made. Additional diagnostics to diagnose HGE may include radiographs, urinalysis, fecal testing or ultrasound.
Causation
HGE may be the result of a pet becoming stressed. This stress could be due to travel, a change in the environment, or a change in diet. Some pets have more sensitive gastrointestinal tracts and stress can induce changes in the flora of their system. This change can allow bacteria to overgrow. An overgrowth of the bacterium *Clostridium perfringens* and the toxins produced by this organism have been implicated. The actual cause of this syndrome is unproven and unknown.
Treatments
AT-HOME CARE
SUPPORTIVE CARE
MEDICATIONS
SPECIALISTS
Cost Of Treatment
The cost of veterinary treatment can vary widely for various reasons, however, HGE requires immediate attention which can mean a visit to the nearest veterinary ER. Treatment costs can range between $500 and $2000 or more depending on the severity of the condition, size of the patient and whether or not hospitalization is required.
Recovery
The prognosis for dogs with hemorrhagic gastroenteritis is good if this condition is discovered early and the bloody diarrhea is treated aggressively with replacement intravenous fluids and other appropriate supportive care. Left untreated, this condition can result in shock, sepsis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, or death. If your veterinarian advises treatment at home, it is imperative you follow up with them if symptoms worsen or do not improve.
Monitoring
Recheck examinations to monitor your pet’s feces and blood work is important to make sure secondary infection has cleared.
Prevention
Unfortunately as the cause of HGE is unknown, it is speculated that anticipation of stressful events and their effect on your dog may aid in prevention of HGE. If your pet has a sensitive gastrointestinal tract, daily probiotics and avoiding situations that may be stressful for them may help prevent HGE.
Disclaimer
The information contained on this page is for educational purposes only. Treatment should only be provided under the advice of a veterinarian who has examined your pet under the laws applicable to your state of residence.

Two Easy Ways to Start Earning Rewards!
Become a member today!Members-only pricing and offers, personalized care notifications, Vital Care points back on every purchase and more!Become a credit card member today!
Earn 2X Pals Rewards points at Petco
when you use Petco Pay!APPLY NOWLearn More About Petco Pay Benefits





